Description
After a solid introduction to the four strokes — intake, compression, power, and exhaust — students are ready to get their hands dirty and see how all of the components work together. They first identify the major and minor components of the cylinder block, then assemble the internal and external parts such as the piston, crankshaft, camshaft, and flywheel. As the work gets more complex — building the cylinder head, adding a spark plug, mounting the carburetor and fuel tank, installing the muffler and air filter — students become increasingly involved in the intricate and delicate inner workings of the engine.
Loading...
Activities
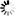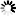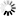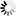
Loading...
Standards
Math/Measure Science Problem Solving Reading
Module Equipment Includes
Student Workbook, Instructor's Manual, Installation CD, Headphones, Organizer Storage Tray (4), Small Engine Workstation, 3 in. Bench Vice, Tool Organizer Tray, Briggs & Stratton Overhead Valve Engine, Tool Chest
Part # and Description
MP8112 Four-Stroke Engine |
| � LTL Shipping Required. |
Requirements
 Loading...
Loading...
Curriculum Specifications
The Building Construction curriculum consists of a well-illustrated student activity guide with 10 daily activities and 5 additional enrichment activities including careers, problem solving, challenge activities, vocabulary reinforcement, and Internet.